Project Overview
Rapidly Exploring Random Trees (RRTs) is a famous algorithm family for solving path/motion planning problems that are generally encountered in robotics applications. They are known to outperform deterministic path planners in highly cluttered/unknown environments due to their probabilistic nature.
The RRT library has been initiated with four RRT variants, each building on top of the previous one:
- RRT: Basic Rapidly-exploring Random Tree.
- RRT*: Asymptotically optimal RRT.
- BiRRT*: Bidirectional RRT* for faster convergence.
- BiRRT* /w Heuristics: Optimized bidirectional search.
The library is implemented in C++ with as much as possible compile-time programming provided through Template Meta-Programming (TMP). Due to its compile-time nature, it is quite efficient when compared to other research candidates.
Visualizations
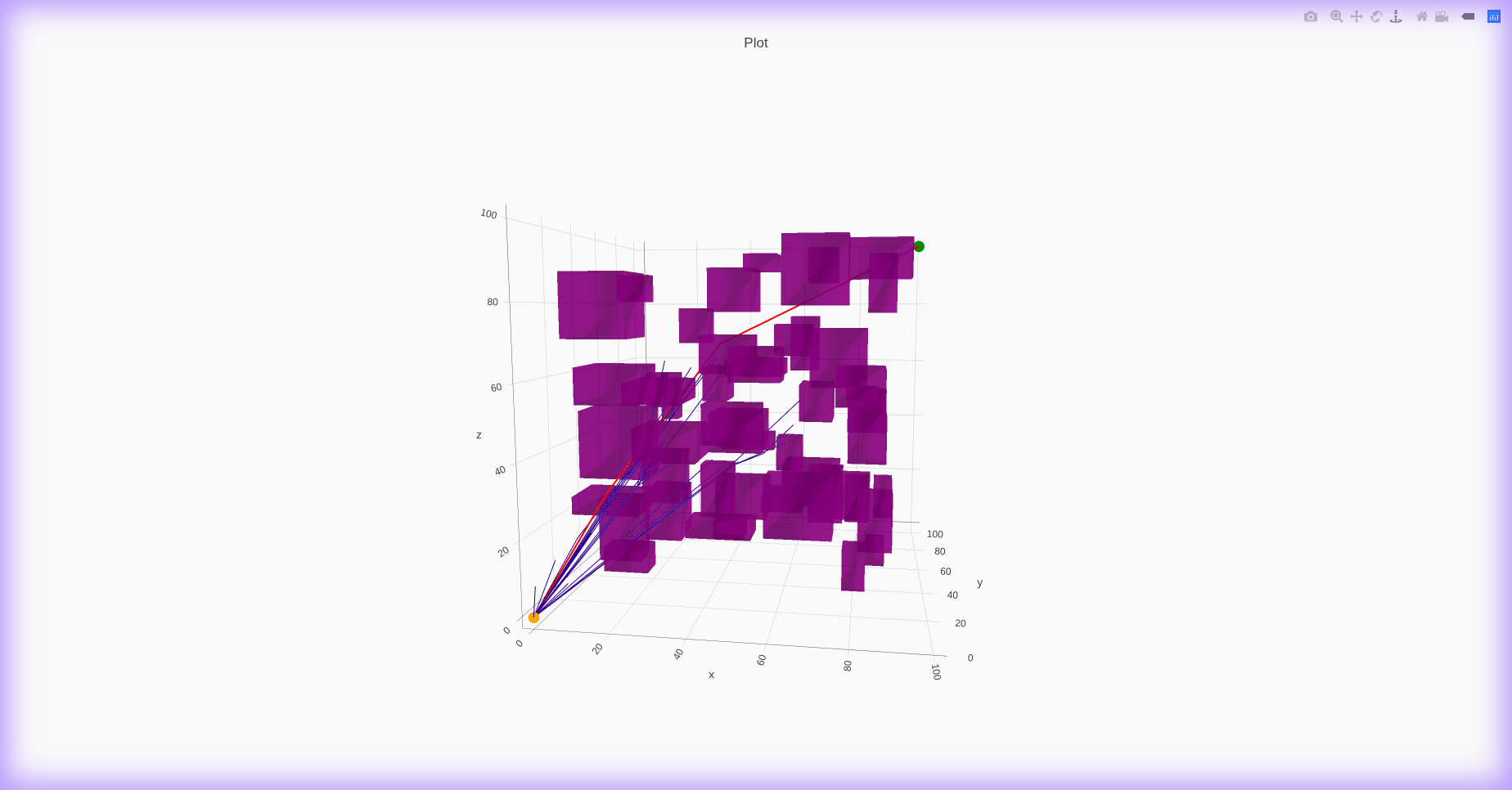
RRT Connect 2D
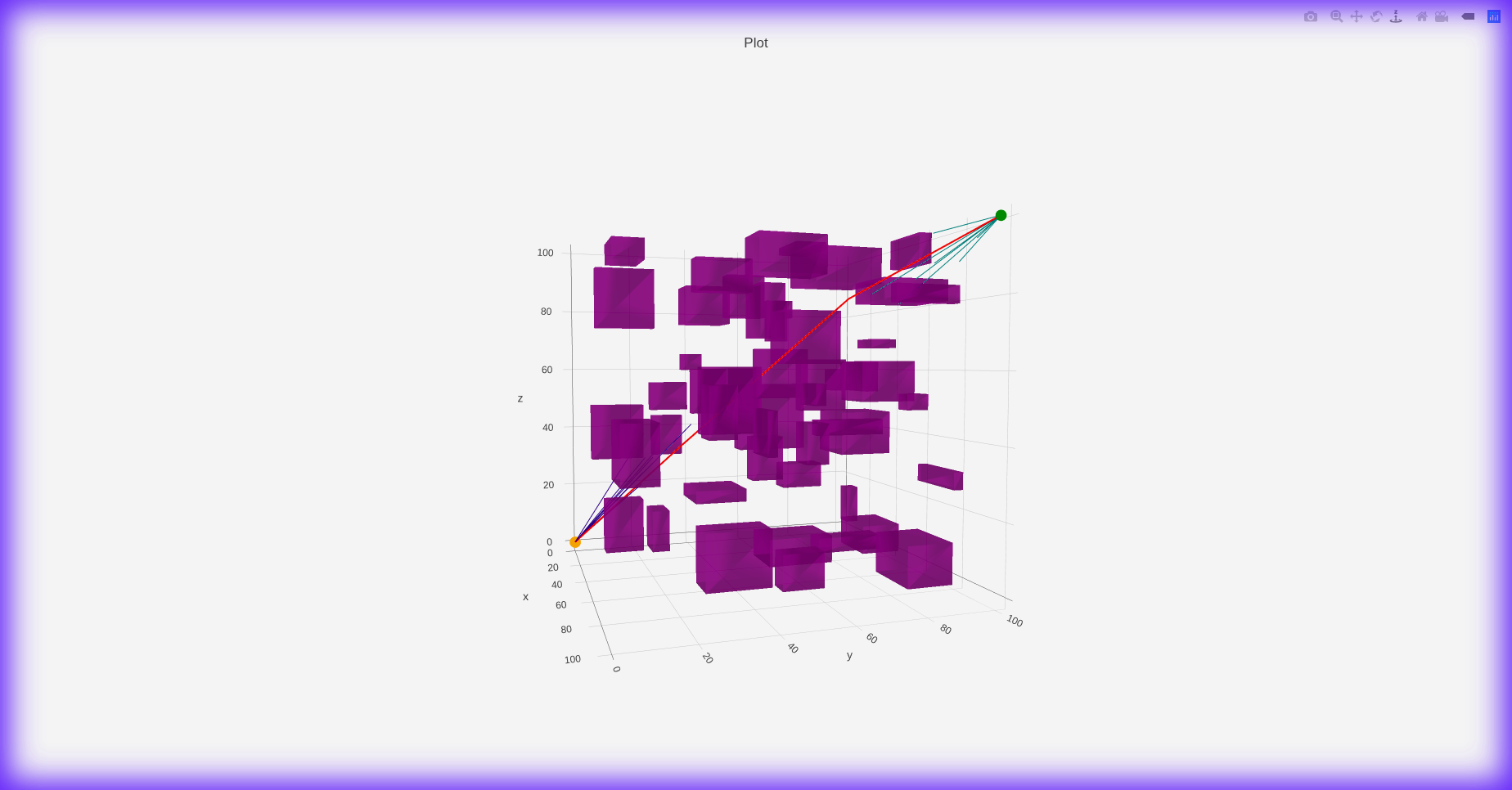
BiRRT* with Heuristics 3D

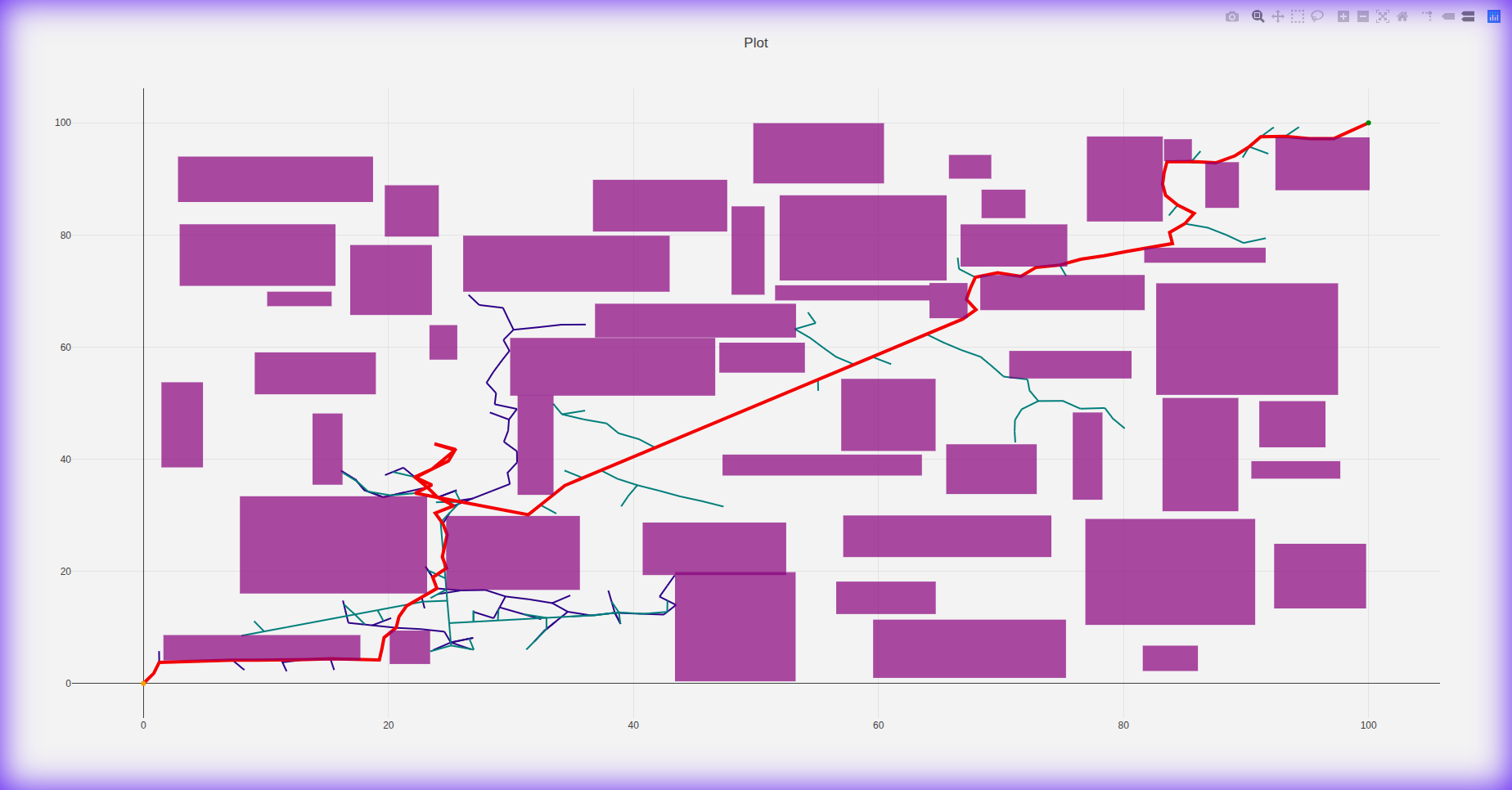
RRT* 2D
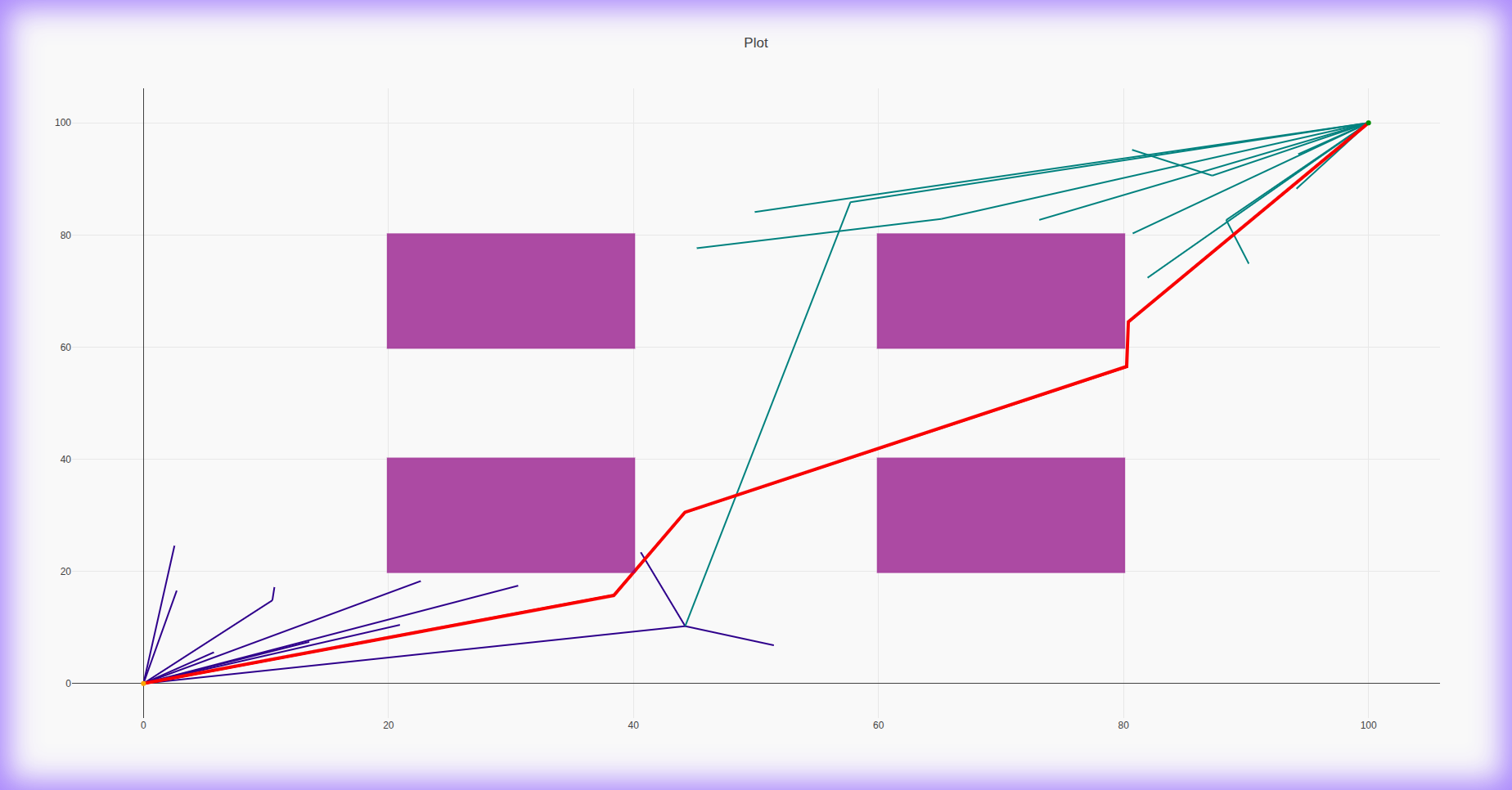
BiRRT* 2D
Technical Details
Boost’s Rtree implementation is used as the underlying fringe for nearest neighbor, search and insert operations. However, for high-dimensional problems, future goals include replacing it with more suitable data structures like Octree or OctoMap.
The project also explores multi-robot motion planning using sRRT and Subdimensional Expansion, aiming to solve complex coordination problems in cluttered environments.